
Security and Malware Vulnerabilities in Bluetooth Low Energy
Check out the official PDF for Security and Malware Vulnerabilities in Bluetooth Low Energy
▱▰▱ Abstract: ▰▱▰
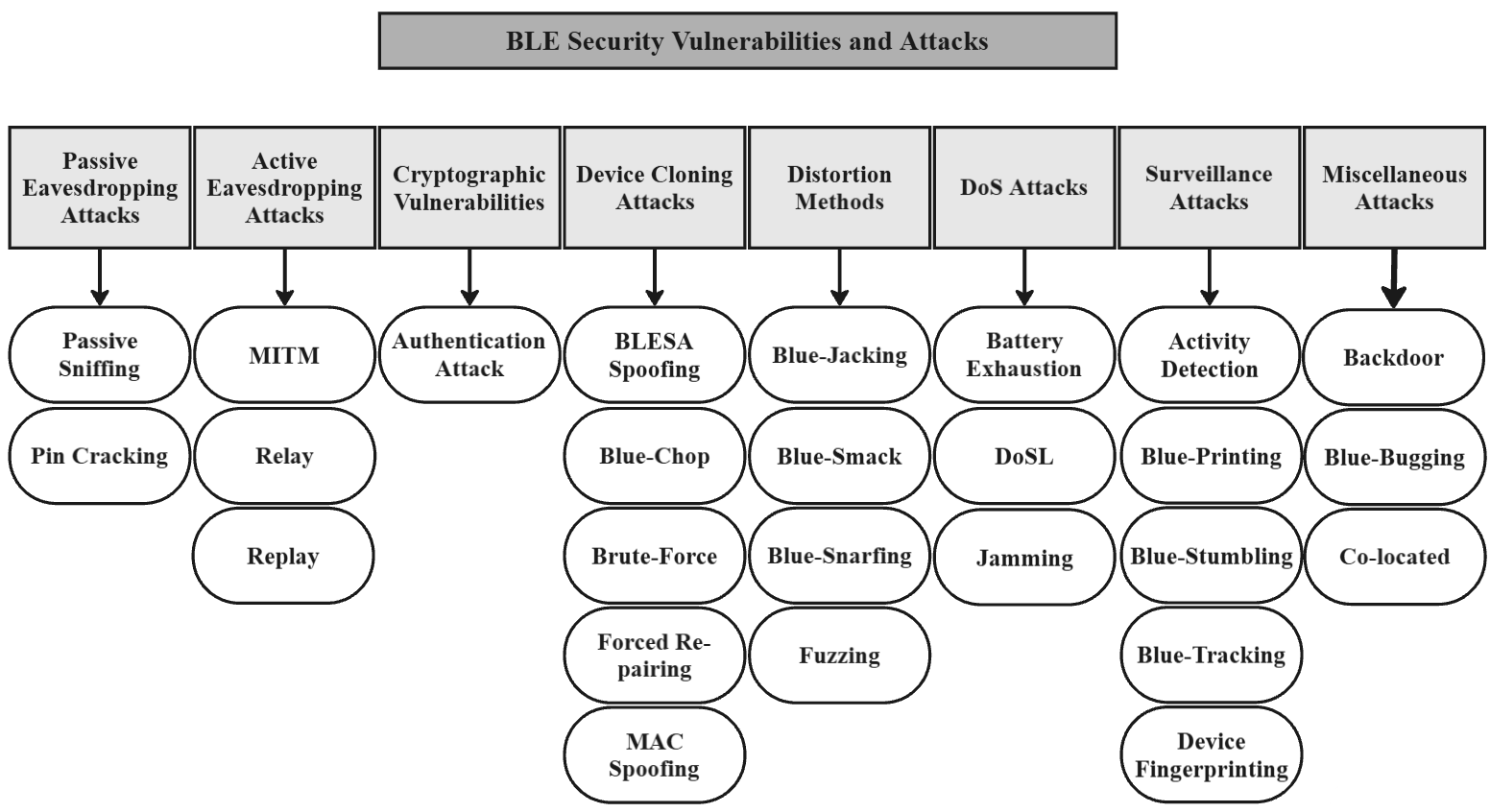
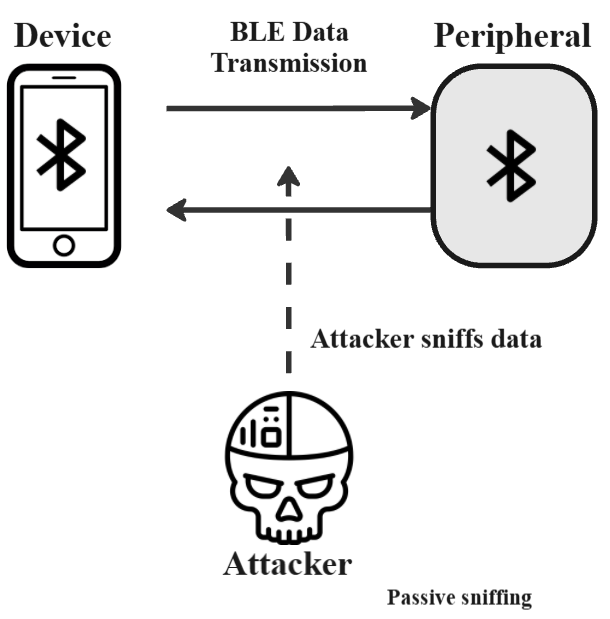
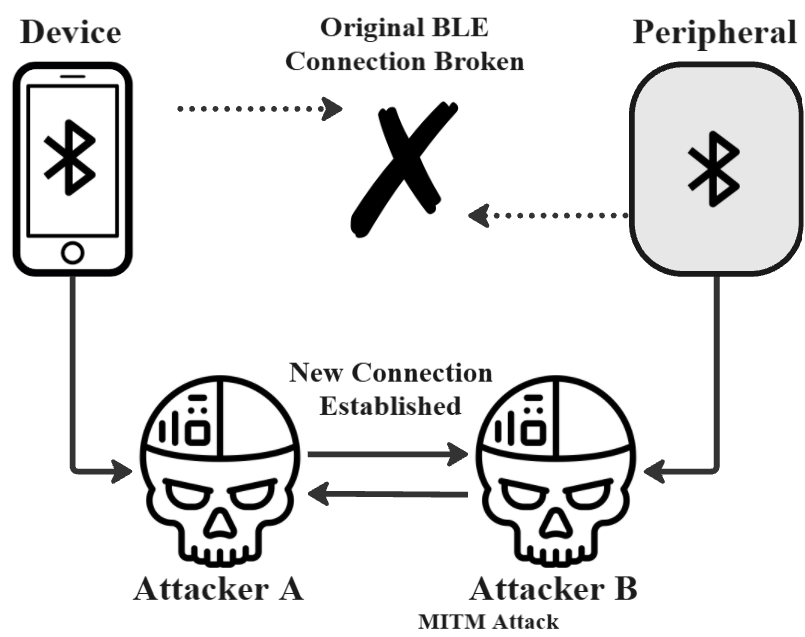
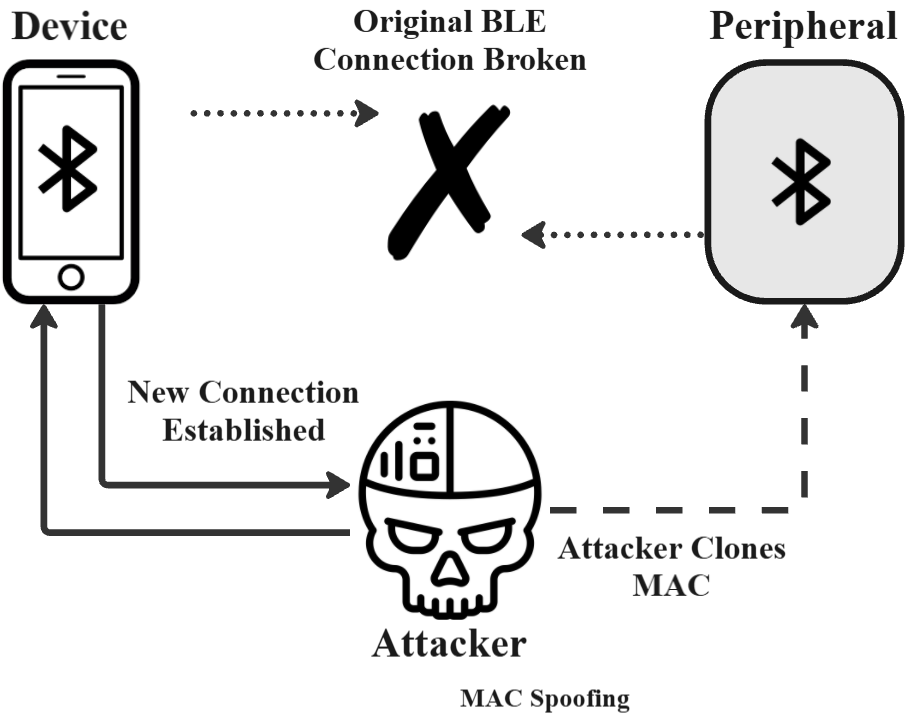
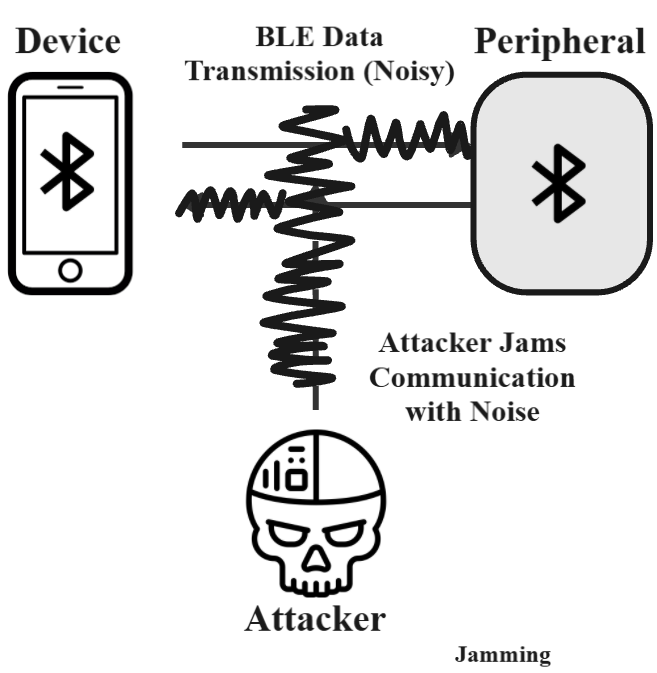
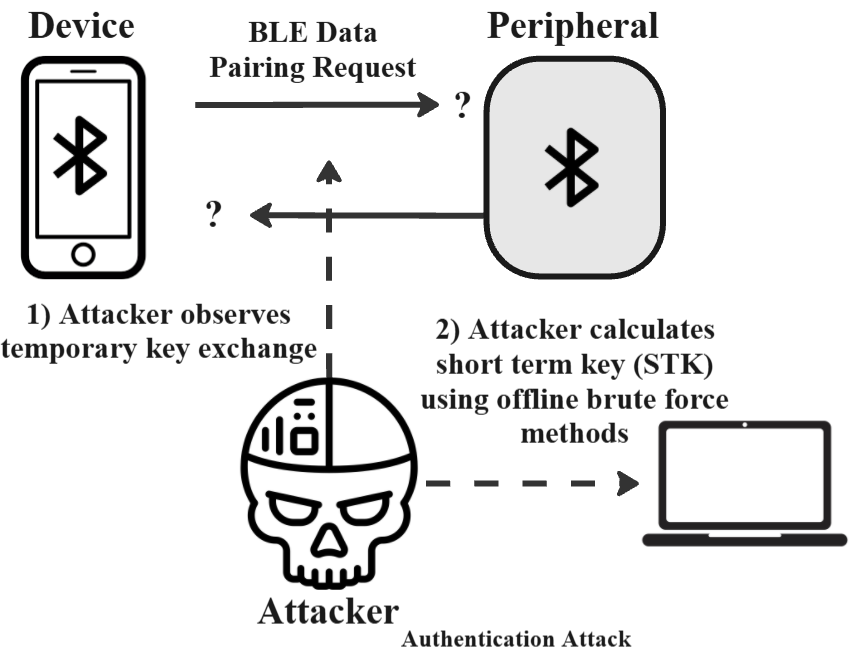
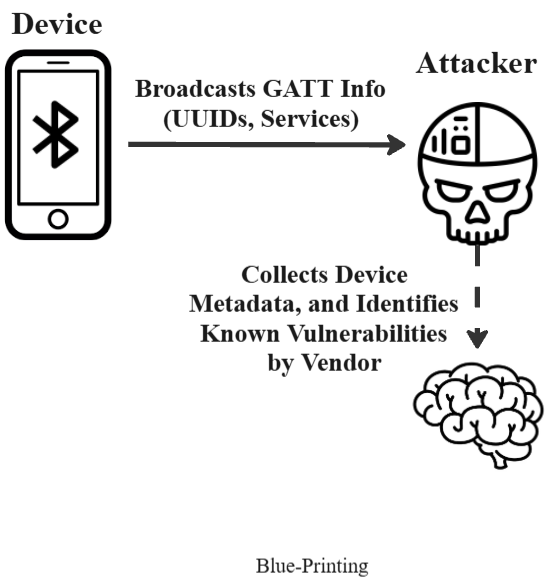
This survey presents a comprehensive study of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) security threats, with a focus on both protocol-level vulnerabilities and implementation flaws across IoT and medical devices. It categorizes attacks including passive sniffing, man-in-the-middle (MITM), DoS, pairing-based attacks, and BLE spoofing. Each threat is supported by academic literature from 14 research papers.
We provide detailed technical explanations, real-world implications, and mitigation strategies for each class of attack. The report concludes with a discussion on persistent limitations in BLE security and future recommendations for protocol improvement and device-side safeguards.
▱▰▱ Methodology: ▰▱▰
Fourteen peer-reviewed papers were selected based on relevance, recency, and breadth of coverage. Each attack type is presented with:
- 1. A technical breakdown of how the attack works
- 2. Known devices and use cases impacted
- 3. Proposed mitigation strategies (when available)
▱▰▱ Discussion: ▰▱▰
Findings highlight the need for:
- 4. Standardized user authentication steps during pairing
- 5. Firmware-level encryption enforcement for stored credentials
- 6. More restrictive BLE stack designs at the OS level, especially for Android
- 7. Improved BLE protocol design to isolate paired device trust zones


